Carbon Cycle WorldAtlas

Carbon Cycle Map Diagram Quizlet
carbon cycle, in biology, circulation of carbon in various forms through nature. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds, many of which are essential to life on Earth.The source of the carbon found in living matter is carbon dioxide (CO 2) in the air or dissolved in water.Algae and terrestrial green plants are the chief agents of carbon dioxide fixation through the process of.
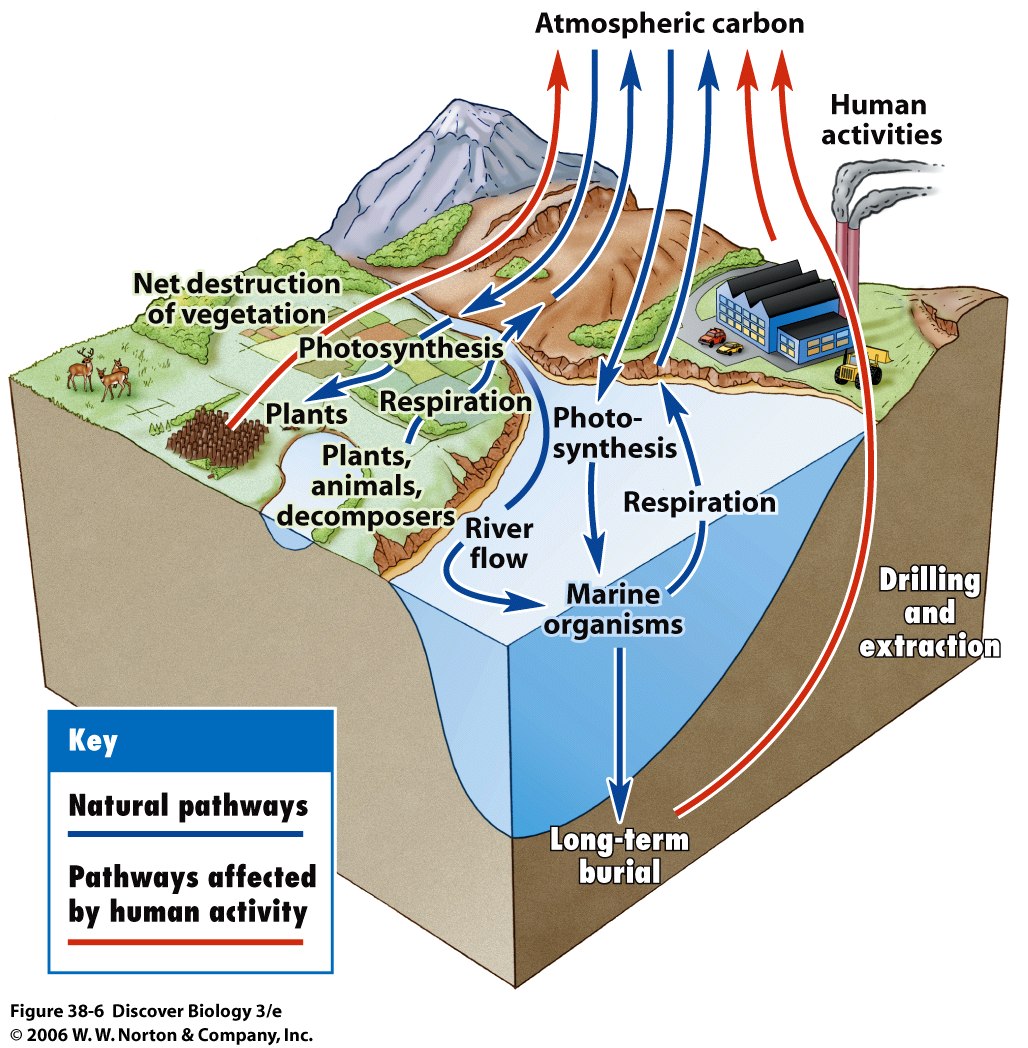
BIO 7 Preview for May 6
Source: Diagram adapted from U.S. DOE, Biological and Environmental Research Information System. This diagram of the fast carbon cycle shows the movement of carbon between land, atmosphere, and oceans. Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, and red are human contributions in gigatons of carbon per year. White numbers indicate stored carbon.

Ecosystems Revision Cards in A Level and IB Biology
The Slow Carbon Cycle. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity, carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks, soil, ocean, and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle. On average, 10 13 to 10 14 grams (10-100 million metric tons) of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year.

Carbon Cycle Diagram Quizlet
Abstract. Black carbon (BC) is produced by incomplete combustion of biomass by wildfires and burning of fossil fuels. BC is environmentally persistent over centuries to millennia, sequestering.
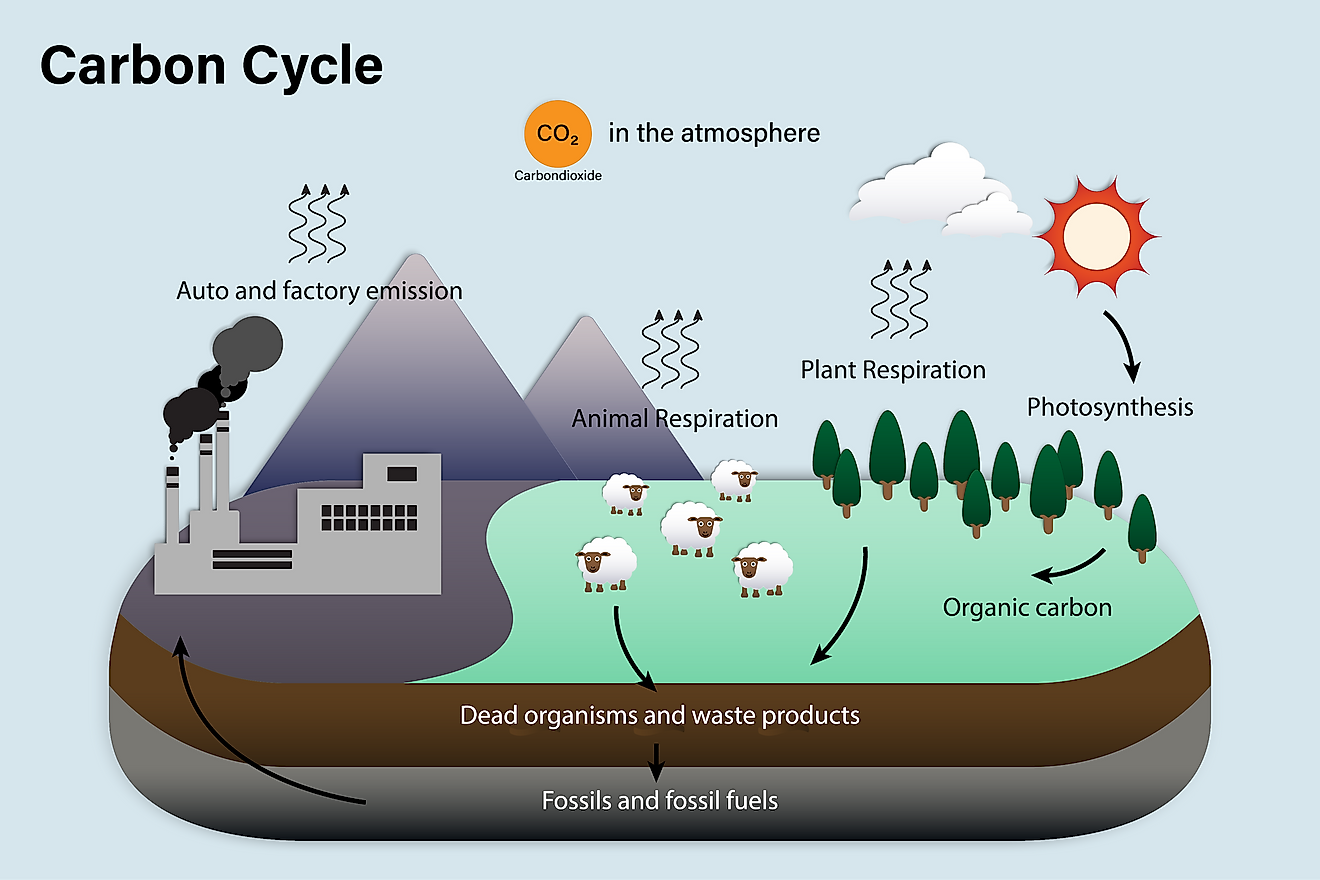
Carbon Cycle WorldAtlas
The carbon cycle is an essential part of How the Earth System Works. Click the image on the left to open the Understanding Global Change Infographic. Locate the carbon cycle icon and identify other Earth system processes and phenomena that cause changes to, or are affected by, the cycling of carbon.. A simplified diagram showing some of the.

ecology quiz carbon cycle Diagram Quizlet
Find the perfect carbon cycle diagram black & white image. Huge collection, amazing choice, 100+ million high quality, affordable RF and RM images. No need to register, buy now!
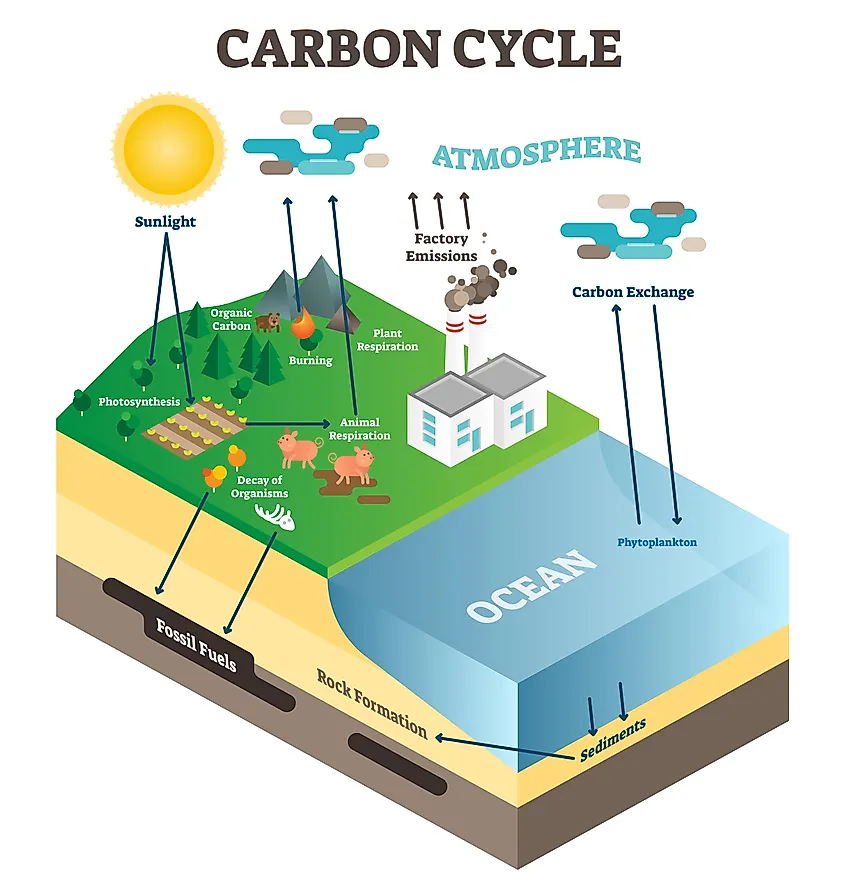
Carbon Cycle WorldAtlas
The carbon cycle is that part of the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth.Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle.Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone.

The Carbon Cycle UCAR Center for Science Education
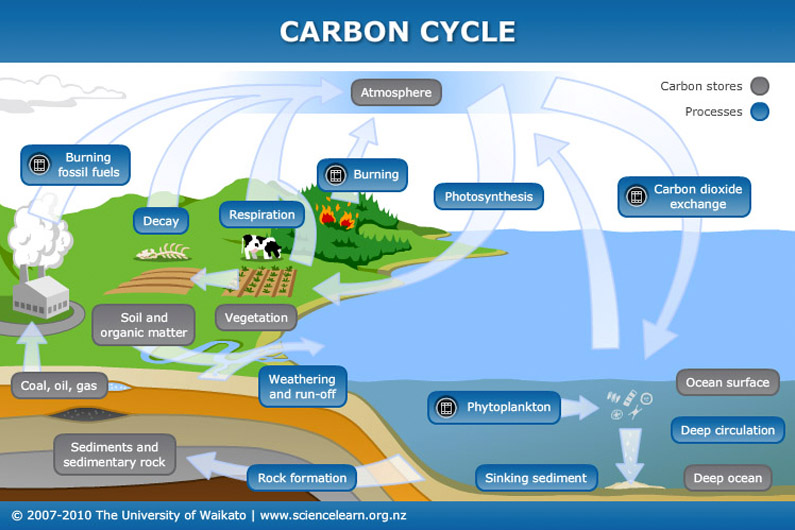
Detailed Description. Carbon cycles through natural systems. Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere as a gas. Plants and animals take in and release carbon dioxide through respiration. Human activities involving fossil fuels, including manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere in large amounts.

Soil carbon Environment, land and water Queensland Government
Systems Thinking. A system is a set of components that are linked through interconnections and functions to create an outcome. The interconnections of components and their interactions create system behavior. This is a broad definition and it describes systems in biology (like the circulatory system or nutrient cycling), a game system (like chess, cards, or football), and even a social system.

Carbon and Forests
The process of photosynthesis involves the absorption of CO 2 by plants to produce carbohydrates. The equation is as follows: CO 2 + H 2 O + energy → (CH 2 O) n +O 2. Carbon compounds are passed along the food chain from the producers to consumers. The majority of the carbon exists in the body in the form of carbon dioxide through respiration.

Carbon cycle Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
Carbon Cycle Diagram. This fairly basic carbon cycle diagram shows how carbon atoms 'flow' between various 'reservoirs' in the Earth system. This depiction of the carbon cycle focusses on the terrestrial (land-based) part of the cycle; there are also exchanges with the ocean which are only hinted at here. Note that carbon atoms are incorporated.

The Carbon Cycle Carbon Positive Australia
Black carbon [HN1] is a product of incomplete combustion of vegetation and fossil fuels. It is ubiquitous and can be found in soils, ice, sediments, and the atmosphere. The interest in black carbon is manifold and includes its aerosol form as the main light-absorbing constituent [HN2], in sediments and ice cores that reveal fire history [HN3], as a sink of atmospheric CO2 in the short-term.
The Carbon Cycle Farm Carbon Toolkit
In fossil fuels, the carbon is stored in long-chain hydrocarbons, and then through combustion with oxygen in our cars or in factories, the carbon is converted to CO 2, which is released to the atmosphere. And in addition, a number of other byproducts are also produced through inefficiencies in combustion like CO which are atmospheric pollutants.
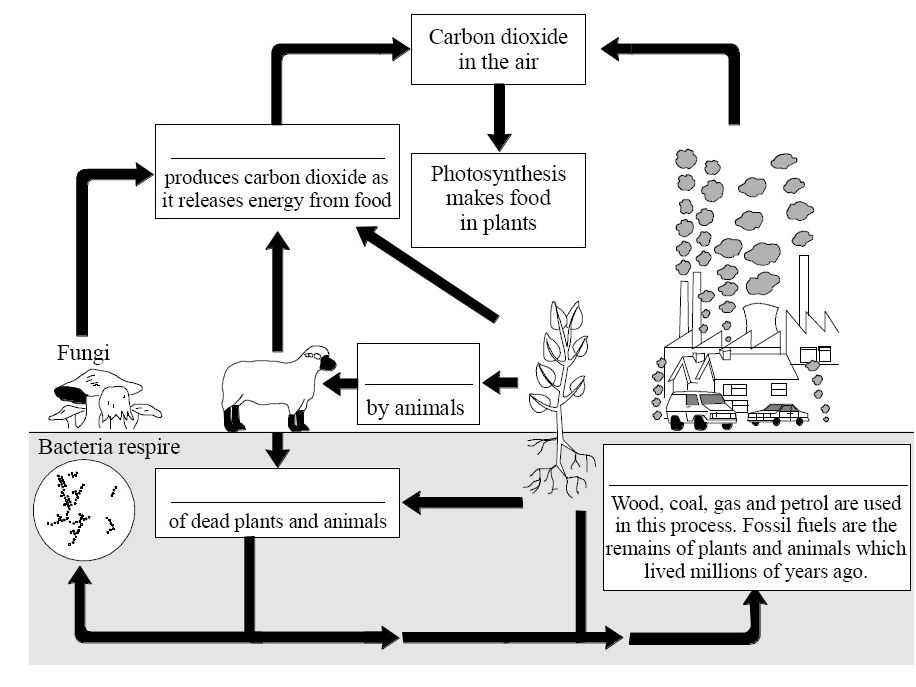
Carbon Cycle question sheets Teaching Resources
The global carbon cycle and anthropogenic CO 2 The global carbon cycle operates through a variety of response and feedback mechanisms. The most relevant for decade to century time-scales are listed here. Responses of the carbon cycle to changing CO 2 concentrations • Uptake of anthropogenic CO 2 by the ocean is primarily
How Does Carbon Dioxide Cycle Through the Oceans? Communicating
Carbon cycle; Environmental chemistry; A full spectrum of colour-based descriptions has emerged to describe the properties and distribution of organic carbon: black, brown, red, blue, green and.

The Carbon Cycle Diagram Quizlet
Organic molecules made by photosynthesizers are passed through food chains, and cellular respiration converts the organic carbon back into carbon dioxide gas. A drawing of mountains, rocks and the ocean titled the carbon cycle. At the top of the drawing above the clouds there is a label of carbon dioxide in atmosphere.